Why Quad Tendon Healing Matters in ACL Reconstruction
In ACL reconstruction using a quadriceps tendon autograft, clinical focus often centers on graft placement and tunnel fixation. Yet, the healing of the quad tendon donor site plays a key role in patient recovery, impacting pain, strength, and long-term functional outcomes.
While quadriceps tendon autografts are associated with favorable morbidity profiles compared to bone–patellar tendon–bone or hamstring grafts, they are not complication-free. Peer-reviewed studies and clinical registries have reported:
- Early extensor mechanism weakness that may persist up to 12–24 months post-op, particularly in active patients or those undergoing revisions (Servant, 2024)
- Anterior knee pain and strength deficits, impacting return-to-sport timelines and overall rehabilitation (Chahla et al, 2023)
- Structural healing concerns when the paratenon is disrupted, prompting newer surgical techniques aimed at biologic preservation (Sherman et al., 2024)
Biologic Rationale for ROTIUM in Quad Tendon Repair
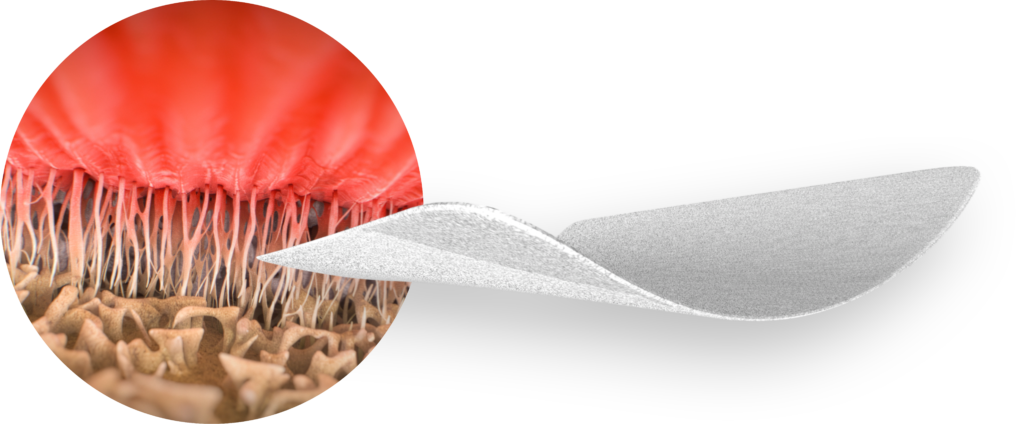
ROTIUM® Bioresorbable Wick is a 100% synthetic, nanofiber scaffold developed to support tendon and tendon-bone healing. Initially FDA-cleared for rotator cuff repair, ROTIUM has gained expanded clearance for use in a broad range of acute and chronic tendon repairs, including the knee.
ROTIUM is designed to:
- Wick 469% of its weight in autologous fluids, including marrow and whole blood
- Resorb over 3-4 months, delivering organic acids into the microenvironment to promote healing
- Serve as a biologic scaffold to drive cellular proliferation and collagen remodeling
- Enhance the healing environment to support more organized, native tissue integration
The unique electrospun matrix mimics the native ECM structure of healing tendon and resorbs over time, leaving behind natively remodeled tissue—not scar.

Technique Integration: Dr. Golan’s Approach
In a VuMedi technique video, Dr. Elan J. Golan demonstrates how to incorporate ROTIUM into ACL reconstruction without disrupting workflow:
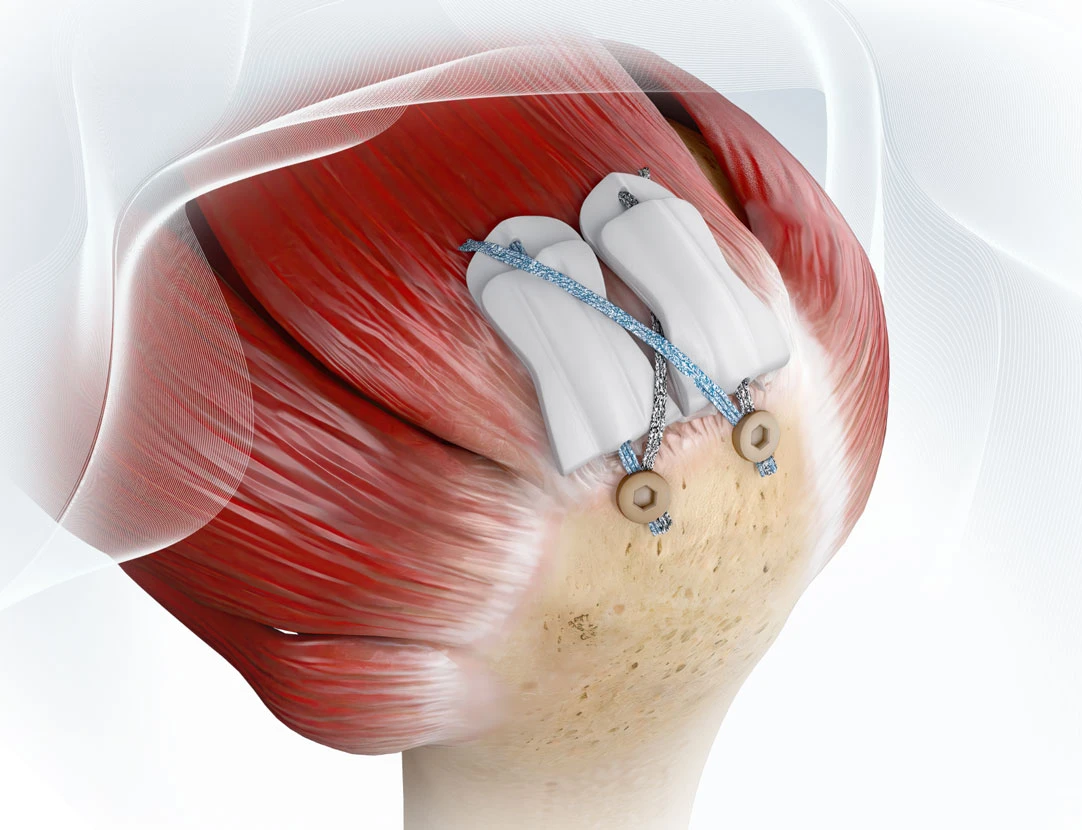
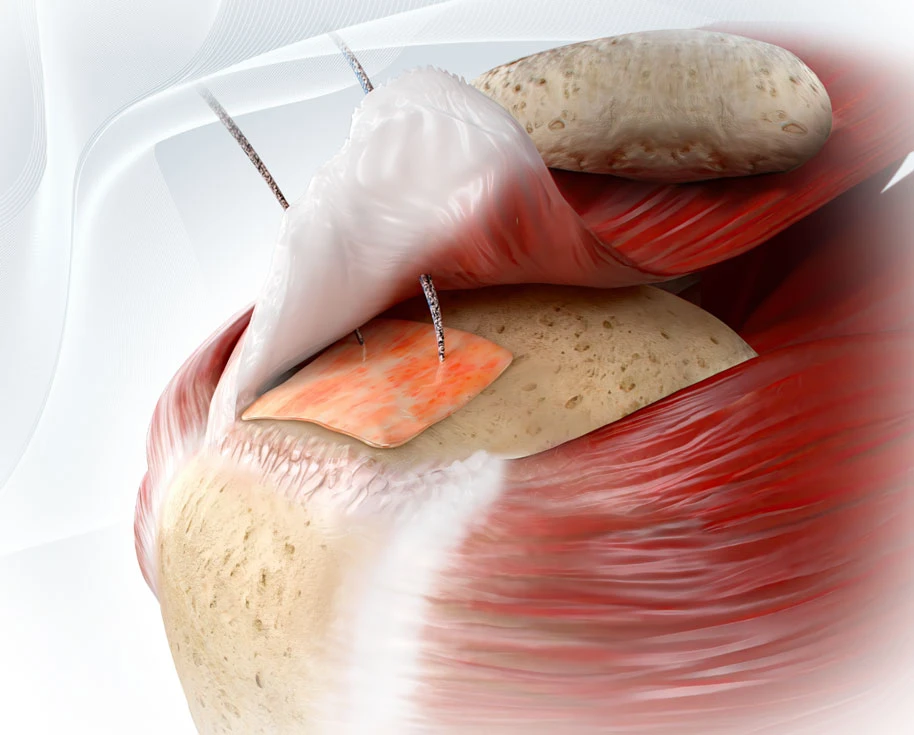
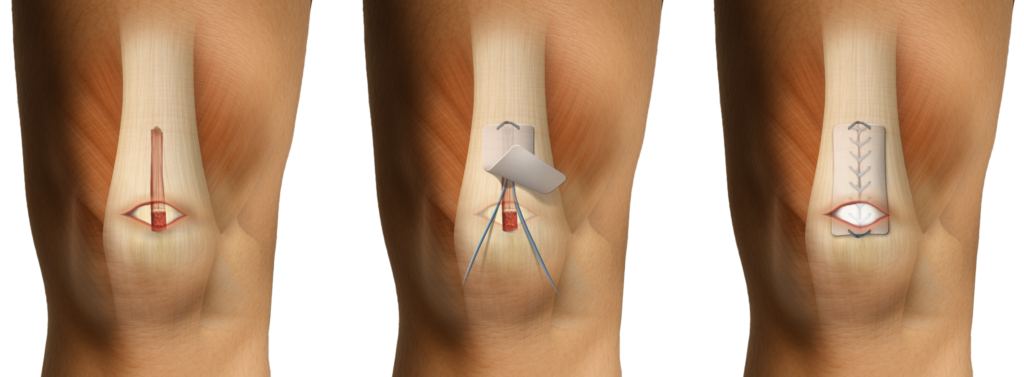
- Harvest the quadriceps tendon in a standard fasion and repair partial thickness defect proximally (with the assistance of a Scorpion device)
- Pass a trimmed ROTIUM scaffold along each tail of the suture and parachute down to the most distal aspect of the quadriceps defect
- Secure the proximal portion and perform closure of the remainder of the partial thickness defect in standard fashion
- Pass the sutures closing the distal aspect of the defect back through the scaffold reduce it down directly on top of the quadriceps repair
- Note: The remainder of the trimmed portion of the scaffold can be incorporated into the distal and proximal ends of the graft to augment the bone-tendon contact in the tibial and femoral tunnels. Importantly, this does not alter the standard preparation nor does it add time to the preparation of the graft.
Clinical Insight
Early healing support is especially relevant in athletes, revision cases, or patients with impaired biology. ROTIUM is engineered to optimize the environment where healing begins. Its use may be particularly valuable in helping reduce variability in recovery timelines, especially where strength restoration and graft protection are priorities. Importantly, the scaffold integrates easily into existing workflows and does not add meaningful surgical time or complexity.